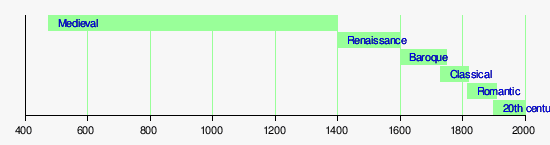
The Classical Era in music is one of the most celebrated periods in Western Art Music. This period, which lasted from around 1750 to 1825, was marked by incredible advances in composition and performance. During this time, many of the most famous composers in history lived and worked, including Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven. In addition to these masters, the Classical Era was also home to some of the most iconic architecture, paintings, and sculptures of all time. Read on and learn about the Classical Era in Music: The Age of Enlightenment.
The Age of Enlightenment
The Classical Era in music was a time in Western Art Music, from about 1750 to 1825. It followed the Baroque Era which was from 1600 to 1750. This new period of Western Art Music was a time of great change and transformation in society and the arts. Through the great minds of the time came the Age of Enlightenment sometimes called The Age of Reason.
As a prelude to the subject of this article, let’s first set the stage for what was going on during this period in history. We were in a period of aggressive scientific, political, and philosophical thinking. This thinking was believed to help create better societies along with its people.
The Enlightenment found ideas featuring the value of human happiness. It promoted the pursuit of knowledge obtained by means of reason and the evidence of the senses.
This philosophical thinking produced a long list of ideas to promote such as liberty, progress, toleration, fraternity, constitutional government, and separation of church and state. The Enlightenment thinking was in great contrast to the idea that people needed to adhere to and rely on scripture or church authorities for knowledge.
Amongst the key figures of the Enlightenment were such names as:
- Frederick the Great (1712–1786)
- Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790) Statesman, Inventor, Philosopher
- Voltaire (1694–1778) Writer, Historian, Philosopher
- John Locke (1632–1704) Philosopher, physician
- Francis Bacon (1561–1626) Philosopher
- Rene Descartes (1596–1650) Philosoper
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712–1778)

Reading of Voltaire’s tragedy of the Orphan of China in the salon of Marie Thérèse Rodet Geoffrin in 1755, by Lemonnier, c.

Palladian Architecture – United States Capitol Building
Classical Era Architecture, Sculpture, and Painting
The Classical era was home to some of the most iconic pieces of architecture, sculpture, and painting that have ever been created. These include the Parthenon, the Sistine Chapel, and the Mona Lisa.
Architecture
Architecture during the classical era can be divided into three main types. Temple-Style, Palladian, and Classic Block.
- Temple-Style – identified by the continuous line of columns around a building. Two famous temple-style buildings of this period are the Panthéon in Paris, by Jacques-Germain Soufflot, and the British Museum in London, by Robert Smirke.
- Palladian architecture comes from the villas of Andrea Palladio. He is known as the greatest architect of the late Renaissance. The most famous Palladian architect during the Classical Era was Britain’s Robert Adam.
The most famous of all Palladian buildings are two American civic buildings, the White House and the United States Capitol. Both were constructed over long periods under various architects.
- Classical Block buildings feature large rectangular (or square) design, with a flat roof and an exterior rich in classical detail. The overall look of such a building is an enormous, classically-decorated rectangular block. Two names stand out in the field of “classical block” buildings. Henri Labrouste designed the Library of Sainte-Geneviève. Charles Garnier created the most famous classical block of all with the Palais Garnier, a Neobaroque opera house.
Sculpture
Neoclassical statues and sculpture first arose in the latter half of the 1700s and was a reactionary style that wanted to rid itself of some of the more frivolous design elements of the preceding Rococo style. Neoclassicism sculptures were heavily influenced by the work of the ancient Greeks and Romans. Advancements in the field of archaeology uncovered magnificent artworks from classic antiquity that the contemporary architects of the time wanted to emulate.
Italian sculptor, Antonio Canova – arguably the greatest exponent of Neoclassical sculpture – was famous for his marble sculptures of delicate nudes. Working after the excesses of the Baroque style, he carved a niche for himself in the world of neoclassical art.
Painting
Neoclassicism appealed to artists supportive of the French Revolution, given the democratic legacy of ancient Greece and Rome. Such artists included Jacques-Louis David, the foremost of all classical era painters. David’s first great work was Oath of the Horatii, which depicts three legendary warriors pledging allegiance to the Roman Republic.
Joseph Mallord William Turner, whose works typically feature a dense, dreamy atmosphere, is often considered England’s greatest painter. As his career progressed, Turner increasingly sacrificed physical realism for rich textures of mist and light, thus foreshadowing the rise of modern art.
Five other famous painters from the Classical Era were:
- William Blake
- Henri Matisse
- Vincent Van Gogh
- Claude Monet
- Pablo Picasso

Characteristics of the Classical Era in Music
Two of the key composers of the Baroque period were: Johann Sebastian Bach and George Fredrick Handel. Many scholars describe this music as very sophisticated. Like the “Fugue”! Detailed and complicated counterpoint.
The Baroque was about expanded harmonies used in the masterpieces of Bach and others. In contrast the Classical Era music was not complicated, but exact. This was a time when people wanted to be entertained and amused. Defined rules for composers to abide by.
Below is a list of some of the highlights of the classical era.
- Less sophisticated forms (Fugues, complicated counterpoint)
- More attention to the melody, Major and minor
- Simplistic harmonies
- Rhythms were very regular and flowing/sudden changes in the long note and shorter note values.
- The texture was mostly homo-phonic with occasional polyphonic.
- Expansion of the orchestra
- Musical genres were written to be more entertaining and fun.
- Dynamics were added
- Occasional use of Trills and Turns
- Much more emphasis on writing for the orchestra as a medium for performance
- Instrumentation: The strings were divided into first and second violins, violas, cellos, and basses.
- The piano replaced the harpsichord and clavichord and became more prevalent during this period.
- Melodies: Simple, singable melodies were favored during the Classical period. These were often in the form of folk tunes or patriotic songs.
- Harmony: The use of counterpoint became more widespread during the Classical period. This is when two or more melodies are played at the same time, often in different octaves.
- Form: The Classical period saw the rise of new musical forms, such as the sonata and the symphony. These were more complex than the forms that came before them, and they often had several movements.
- Tempo: During the classical age, tempo markings became more common. This helped to ensure that the music was played at the proper speed.
- Rhythm: The rhythm became an important element during the Classical period. This is when composers began to use different rhythms in their music to create a more expressive sound
Major Composers of the Classical Era
The year was 1750. This was the year that Johann Sebastian Bach died. What is significant about this centers around the fact that it claimed the end of the Baroque Era and the beginning of the Classical Era in Music
Three composers paved a new road for popular music. Music that would be studied and performed hundreds of years later. Their names would be recognized by young and old alike.
- Franz Joseph Haydn
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
- Ludwig Van Beethoven
Composers like Haydn and Mozart thought that Bach was too old-fashioned. They felt that his music was very technical and complicated. Baroque music was too heavy, not fun. You might say, Baroque music was for the composer and musician, and Classical Music was for the people. Musical compositions to listen to and enjoy!
Franz Joseph Haydn
Joseph Haydn was an Austrian composer. Many scholars have called him the main architect of the classical period. Haydn was called the “Father of the Symphony” as he set the platform for writing this musical genre. He was responsible for the development of Chamber Music and his creation of the “String Quartet.” Over his long and successful career, Haydn composed roughly 750 compositions in various genres. Below is a partial list of some of his accomplishments:
- 108 Symphonies
- 68 String Quartets
- 47 Piano Sonatas
- 20 Operas
- 14 Masses
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Melody is one of the five basic elements of music. Composers were writing great melodic lines with simple accompaniments. The master of this was Mozart. He would compose melody after melody, making his music sought out by young and old alike. To say that Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a genius is an understatement. At age six, he was already recognized as a child prodigy. Young Wolfgang did concert tours with his sister as they amazed audiences with their piano skills. The Donnie and Marie of the time.
Mozart’s grasp and a keen sense of the fundamentals of music helped him develop an incredible ear. Mozart could listen to a piece of music and write it on paper. To put it bluntly, if Mozart was living today, he would be the biggest rock star of them all.
Ludwig van Beethoven
Beethoven was a German composer and pianist. He was born in December 1770 and died in March 1827. Beethoven is considered by many to be the greatest composer of all time. Along with Mozart and Haydn, he produced an incredible amount of music.
He wrote in almost every genre of the time. His music paved the way for the next era called the Romantic Period. Music scholars worldwide claim him as a “crucial figure in the transition between the classical and romantic periods.” Beethoven was deaf for most of his career. The fact that he composed such great music is amazing.
The performance medium he was most noted for was the Orchestra. He was brilliant at expanding the tone colors of the orchestra. Beethoven did this by increasing the size of the orchestra. He expanded the string and woodwind sections. He produced new bold and intense sounds. His music was also soft, delicate, and contrasting. His nine symphonies remain his most popular and memorable works.
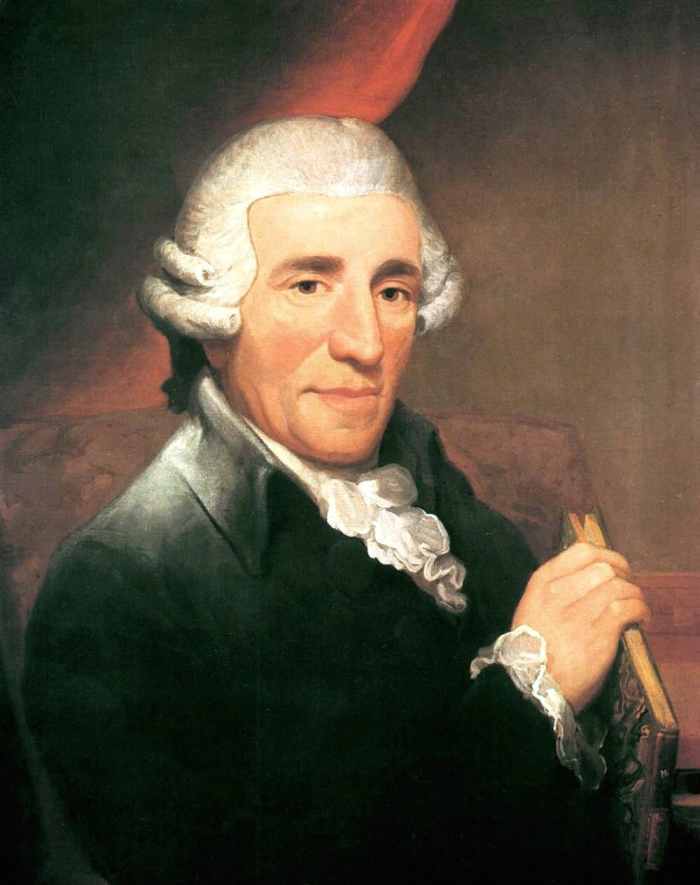

Franz Joseph Haydn
Symphony No. 45 in F sharp minor – Haydn
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Eine Kleine Nachtmusik – Mozart

Ludwig Van Beethoven
Beethoven – Für Elise
Other Composers from the Classical Era
How long with the incredible music produced by Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven were others that contributed great music. A few names were:
- Franz Schubert
- Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach
- Gioachino Rossini
- Muzio Clementi
- Christoph Willibald Gluck
Below is a more defined chronological list of additional composers from the classical era.
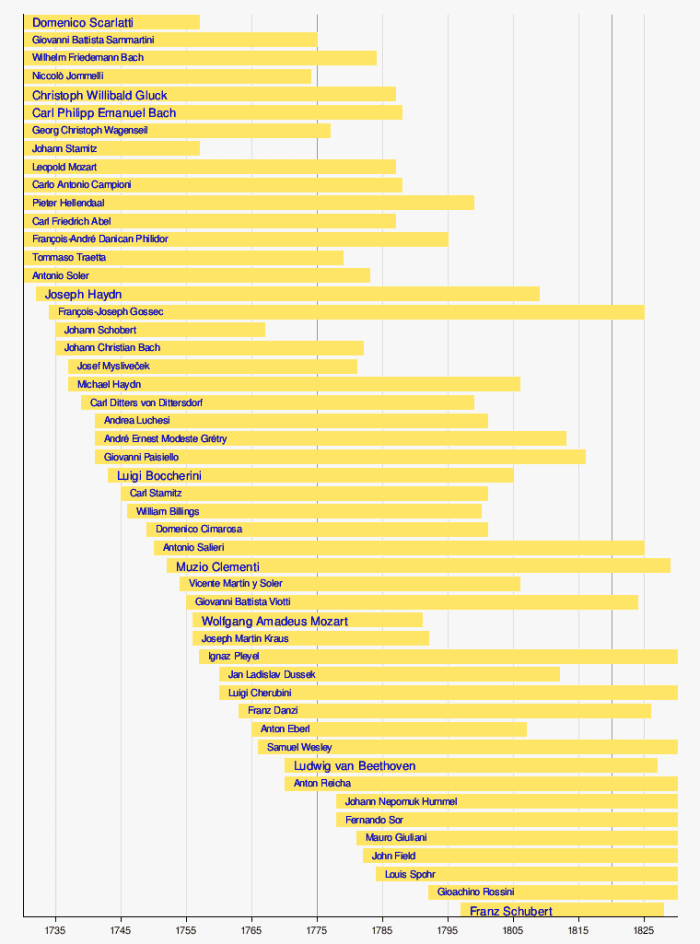
Wikipedia
Genres Developed in the Classical Era
Below is a list of different musical genres developed during the classical period:
- Sonata – a solo composition written for a particular instrument. This featured the special skills of the soloist. Typically written in three or four “movements” with one or more in sonata form. Sonata Allegro – is the first movement of a Sonata. An exciting opening featuring the virtuosity of the performer.
- Symphony – largest form of instrumental music performed by an orchestra. Written in large sections ( typically four) called movements.
- Concerto – similar to the symphony featuring a solo instrument. The orchestra serves as the accompaniment for the soloist. The Concerto is written in several movements.
- Art Song – vocal music written to be performed in a recital. The melody is set to a poem. Known as “Lied” (German).
- Opera – a dramatic work set to music for singers with orchestral accompaniment.
Primary Performance Mediums
- Solo music during the Baroque and Classical periods was routinely composed for many instruments. A common term for “solo instrumental work” is sonata. (Note that “solo music” for a non-keyboard instrument usually features keyboard accompaniment.) During the Classical Era, the piano became the primary keyboard instrument. The harpsichord and clavichord were used less and less.
- Small Ensemble The diversity of instrument combinations in small Ensemble works expanded markedly during the Classical period. Ensembles usually featured some combination of strings, woodwinds, and/or piano.
- Large ensemble music can be classified as orchestral or vocal. The leading forms of orchestral music during the Classical era were the symphony and concerto, while large-scale vocal music was dominated by opera and sacred choral works.
The Orchestra
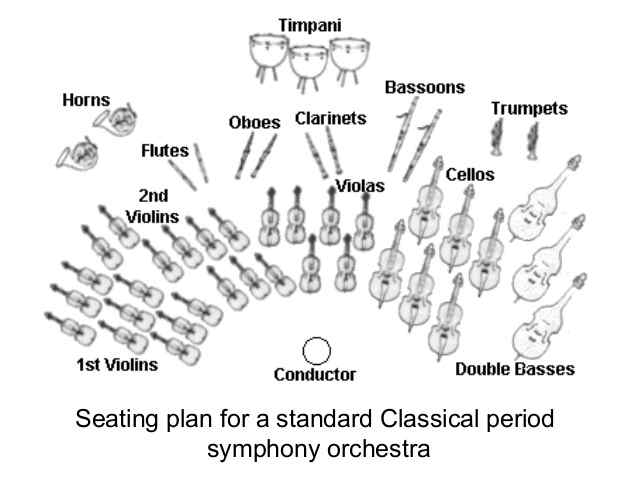
The orchestra was becoming the most popular performance medium of the Classical Period. The music was rich, bold, melodic, and very beautiful.
Like Beethoven, composers found ways to expand tone colors for their music. They changed the orchestra instrumentation to fit their music. Therefore, the much smaller Baroque Orchestra evolved into the Classical Orchestra, as seen below.
One of the most important aspects of the Classical Era was the development of public concerts. Before this period, most music was only heard in private settings, such as noble homes or churches. However, during the Classical Era, composers began writing music specifically for public performance.
Classical Era in Music Listening List
| Name of Composition | Composer | Performance Medium |
|---|---|---|
| Trumpet Concerto in A Flat Major | Haydn | Solo Trumpet/Orchestra |
| Symphony in Bb Major H 658 | CPE Bach | Orchestra |
| Clarinet Concerto in A Major | Mozart | Solo Clarinet / Orchestra |
| Symphony No.94 in G Major | Haydn | Orchestra |
| Symphonies 1-9 | Beethoven | Orchestra |
| Eine Kline Nachtmusik | Mozart | Orchestra |
| Symphonies 4-5 | Schubert | Orchestra |
| Piano Concerto No. 4 in G Major | Beethoven | Piano/Orchestra |
| Symphony No. 48 in C Major | Haydn | Orchestra |
| Ave Maria | Schubert | Vocal |
| String Quartet No. 62 | Haydn | String Quartet |
In Conclusion
As stated at the beginning of this article, the Classical Era in music is one of the most celebrated periods in Western Art Music. One could spend a lifetime learning about the people, places and things of this period of history.
My intention was to give a good overview of the Classical Era in Music: The Age of Enlightenment. It is also with hopes that the reader will appreciate understanding that the classical era defines only a small portion of what makes up what we call “Classical Music” today.
